Menu
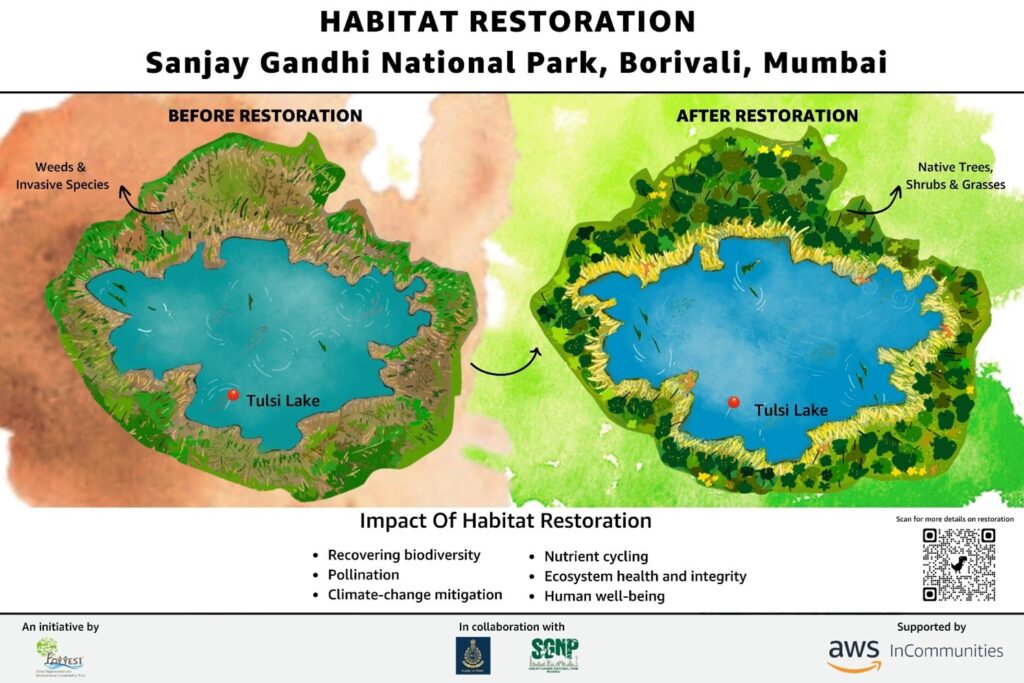
At Sanjay Gandhi national Park the invasive species of Chromolaena odorata is degrading the forest ecosystem slowly over the years. More than 50 Acres of forest is invaded by Chromolaena odorata aptly knows as “Ran-mari” or forest-killer. Through this habitat restoration work at Sanjay Gandhi National Park, Borivali, Mumbai, Chromolaena odorata has been removed from 15 Acres of the core forest area manually as machines can not disturb the core forest area.
After clearing the area of invasive species, 6500 forest trees, shrubs and grasses were restored back in the forest. Flora of Sanjay Gandhi Forest was researched, and 139 native trees and grasses species were selected for this restoration.
The restored area will be maintained for the next three years where weeds will be removed again, and watering will be carried out in the non-monsoon season.
Removal of Invasive species


Land Preparation


Planting native grasses near lake bank

Planting trees and shrubs

Species selection:
Trees were researched for native, original species of Borivali forest. Selected trees, shrubs and grasses are mix of pioneer species, trees which can grow well in nutrient deficient soil, are drought resistant, increases soil carbon and fix nitrogen.
Selected trees have medicinal value, have fruits, flowers and will support forest biodiversity. As trees are local, native forest trees they are extraordinarily strong and not susceptible to pests and diseases.
Selected trees among 139 species include keystone species like Ficus infectoria, Ficus macrocarpa, Ficus racemose, Ficus drupecaea , Ficus tinctoria and trees which are getting rare in Borivali forest like Boswelia serrata, Mammea suriga, Diospyros montana, Lagerstroemia macrocarpa, Pterocarpus marsupium and Hymenodictyon obovatum among others.
Shrubs like Holarrhena pubescens, Maytenus rothiana, Clerodendrum serratum and grasses like Dicanthium annulatum, Pennisetum aleonoides, Desmostachia bipinnata Saccharum sponteneum and Themeda sp were restored back.
With the restoration of original forest faunal species the birds, bats, bees, other insects like beetles, bugs, moths will be increased and in turn and replies, mammal population will increase in the wildlife sanctuary.
This restoration is supported by AWS InCommunities.
